• Different kinds of resources are being used by the farmer in the production process, which are involved in producing farm commodities.
• There are two types of resources involved.
• Mono period resources
* The resources which are used only once to satisfy a need are called mono period resources.
* Eg : Seeds, fertilizers, etc..
• Poly period resources
* The resources which are used time and again are called poly period resources.
* Eg : Farm machinery, farm building etc..

• The estimation of expenses incurred as the result of using mono period resources is easy for the producer.
• Whereas the difficulty arises in estimating the cost of poly period resources.
• Therefore an estimation of cost of services rendered by poly period resources requires an accounting procedure.
• One such methods used is DEPRECIATION.
DEFINITION
" The decline in the value of asset due to usage, accidental damage and time obsolescence. "
MEANING
- When an asset is used over a period of time, it may undergo wear and tear and leads to the reduction in original value of the asset.
- Time, weather, damages etc are the important parameters causing depreciation.
- Similarly, even if the asset is not used, there might be the reduction in the value as it becomes old or outdated. It is known as time depreciation.
- It is important to note that changes in prices do not cause depreciation.
To estimate depreciation, we need
USEFUL LIFE
It is defined as the time period or number of years an asset it used in the farm business.
JUNK VALUE
It is defined as the value of an asset at the end of the age at which it completely wears out.
It is also known as disposal value or scrap value or terminal value or salvage value.
BOOK VALUE
It is defined as difference between the original cost of an asset and the accumulated depreciation.
Book value = original cost - accumulated depreciation
METHODS TO ESTIMATE DEPRECIATION
There are two assumptions to be considered for the estimation of depreciation
I. An asset is put to constant use.
II. An asset is put to varying rates.
1. Straight line method.
2. Diminishing balance method.
3. Sum of the years digits method.
4. Annual revaluation method.
1. STRAIGHT LINE METHOD
- It is based on the assumption of an asset is put to constant use.
- It is most commonly and widely used method as it is very easy and simple.
Annual amount of depreciation =
(original cost of the asset - junk value) useful life of an asset
Example :
The original cost of a Knapsack sprayer is ₹ 2500. The farmer sold it for ₹ 500 over the period of 10 years of it's constant use. Find the annual amount of depreciation for the sprayer.
Solution :
Original cost of the sprayer = ₹ 2500
Junk value of the sprayer = ₹ 500
Useful life = 10 years
Formula
Annual amount of depreciation =
(original cost of the asset - junk value)
useful life of an asset
= 2500 - 500
10
= 2000
10
Annual amount of depreciation = ₹ 200
Inference
In this method, the same annual amount of depreciation i.e., ₹ 200 is charged completely throughout the useful life of ten years.
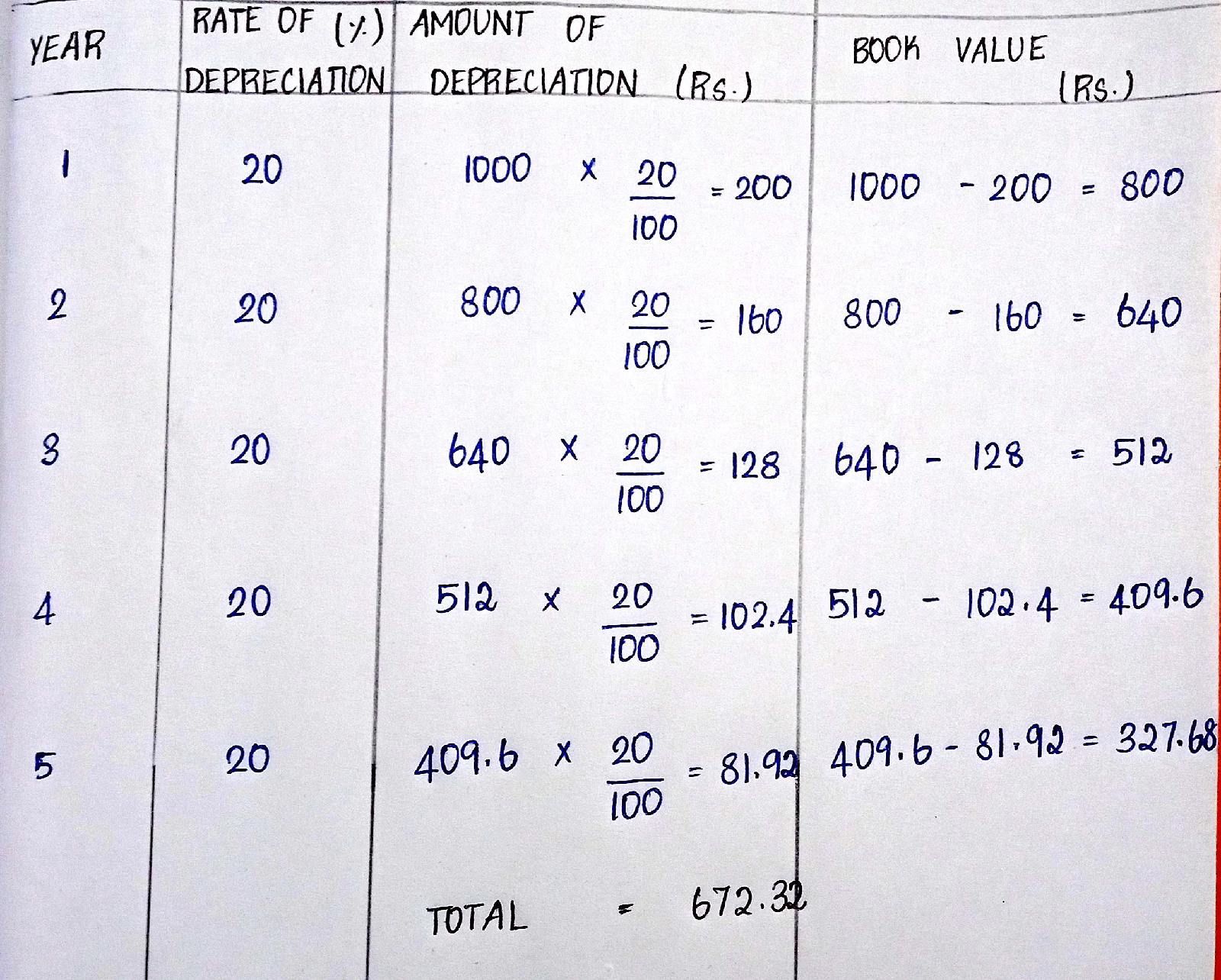
2. DIMINISHING BALANCE METHOD
It is based on the assumption of of an asset is put to varying rates.
Annual amount of depreciation
= ( Book value of an asset x R )
Where,
R - rate of depreciation.
R = n x 100
Useful life
Where,
n - each year the depreciation to be calculated.
Example :
The original cost of a plough is ₹ 1000. The farmer sold it for ₹ 500 over the period of 5 years of it's constant use. Find the annual amount of depreciation for the plough.
Solution :
Original cost of the plough = ₹ 1000
Useful life = 5 years
Rate of depreciation = n x 100
Useful life
= 1 x 100
5
= 20 %
* In this method, the annual amount of depreciation is decreasing from ₹ 200 in the first year to ₹ 81.92 in the fifth year.
* Initial year, higher amount of depreciation is charged because the asset is thoroughly used when it is new.
* Whereas, in the later years as the wear and tear is more the amount of depreciation is less.
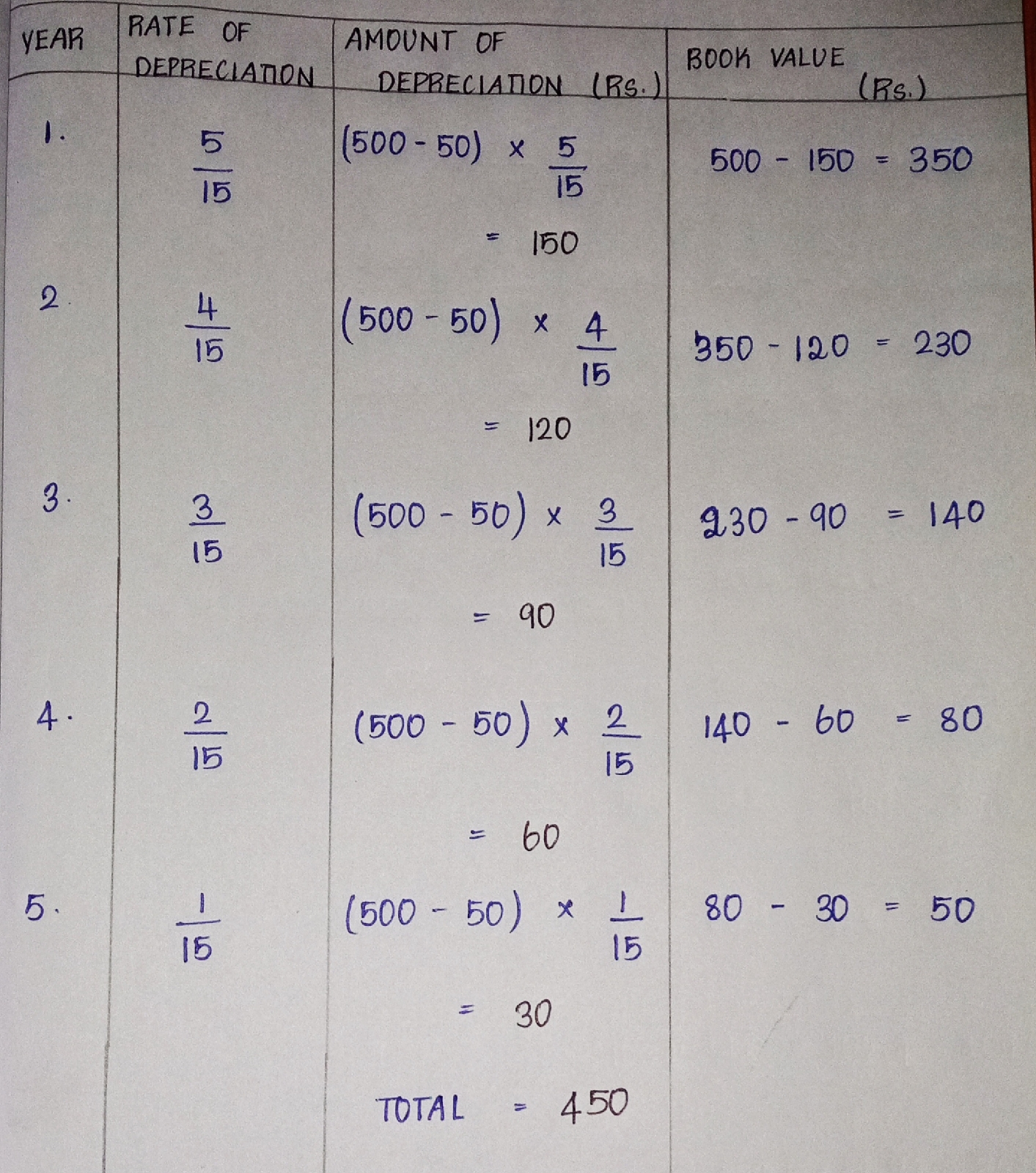
3. SUM OF THE YEARS DIGITS METHOD
This method is based on the assumption of an asset is put to varying rates of you see here after year.
Sum of the digits = n ( n + 1 )
2
Where,
n = 1,2,3,4,........n
Rate of depreciation =
Remaining years of useful life
Sum of the digits of the useful life
Example
The original cost of a spade is ₹ 500. The farmer sold it for ₹ 50 over the period of 5 years of it's constant use. Find the annual amount of depreciation for the spade.
Solution :
Original cost of the spade = ₹ 500
Junk value = ₹ 50
Useful life = 5 years
Sum of the digits = n ( n + 1 )
of useful life 2
= 5 ( 5 + 1 )
2
= 5 x 6
2
= 5 x 3
= 15
Original cost = Total amount of depreciation + junk value
= 450 + 50
= ₹ 500
Inference
* In this method, the annual amount of depreciation is decreasing from ₹ 150 in the first year to ₹ 30 in the fifth year.
* Different amount of annual depreciation is charged with every year.
4. ANNUAL REVALUATION METHOD
• In this method the annual amount of depreciation of the asset is revalued every year.
• Here, the estimation is done at the beginning as well as at the end of the year.
• The difference between this gives the value of depreciation or appreciation.
• This method is not applicable for estimating the depreciation of all assets, as it is difficult to get the market prices for the assets of varying wear and tear expenses.












No comments:
Post a Comment